RDFaCE is an online RDFa content editor based on TinyMCE. It supports different views for semantic content authoring and uses existing semantic Web APIs to facilitate annotating and editing of RDFa contents. As depicted in the following picture, the RDFaCE system architecture consists of three layers: Rich Text Editor, RDFaCE plugin and External Services layer.
RDFaCE supports four different views for semantic text authoring:- WYSIWYG View. What-You-See-Is-What-You-Get- WYSIWYM View. What-You-See-Is-What-You-Mean- RDF Triple View.- Source Code View.
The views are synchronized such that changes made in one of the views automatically update the others.
- About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
- 02 Edit PDF text. Go to the 'Edit' tab and you'll find a complete toolset to edit your PDF document. To edit text, you just need to click the 'Edit' button to open the editing mode (you can switch between two different editing modes: 'Line Mode' and 'Paragraph Mode' ), then you can edit any piece of text in the document by tapping on the place where you want to edit.
- Written and maintained by Nicholas Humfrey. The library is licensed under the BSD 3-Clause license and documentation under CC BY 3.0. The examples are in the public.
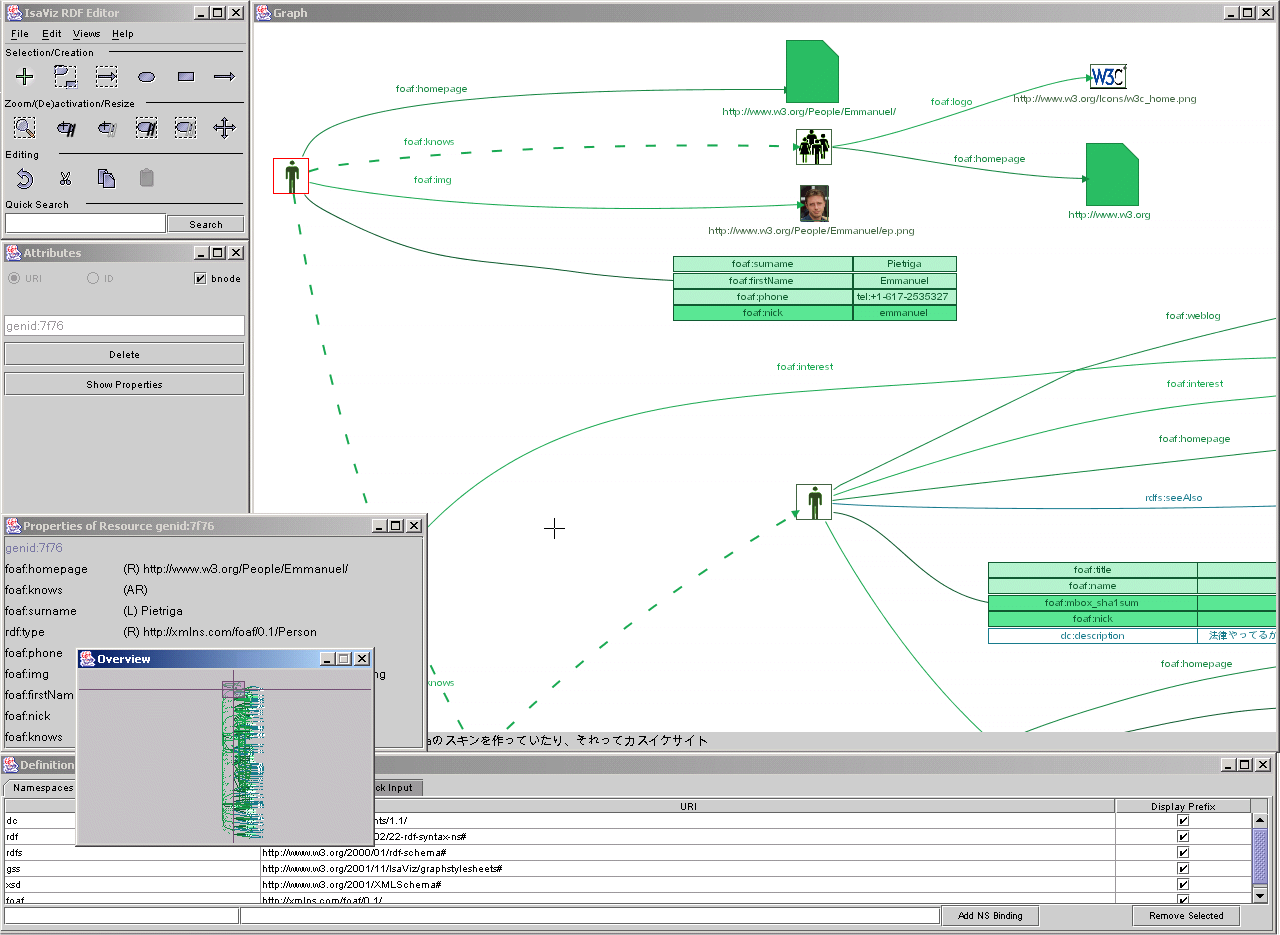
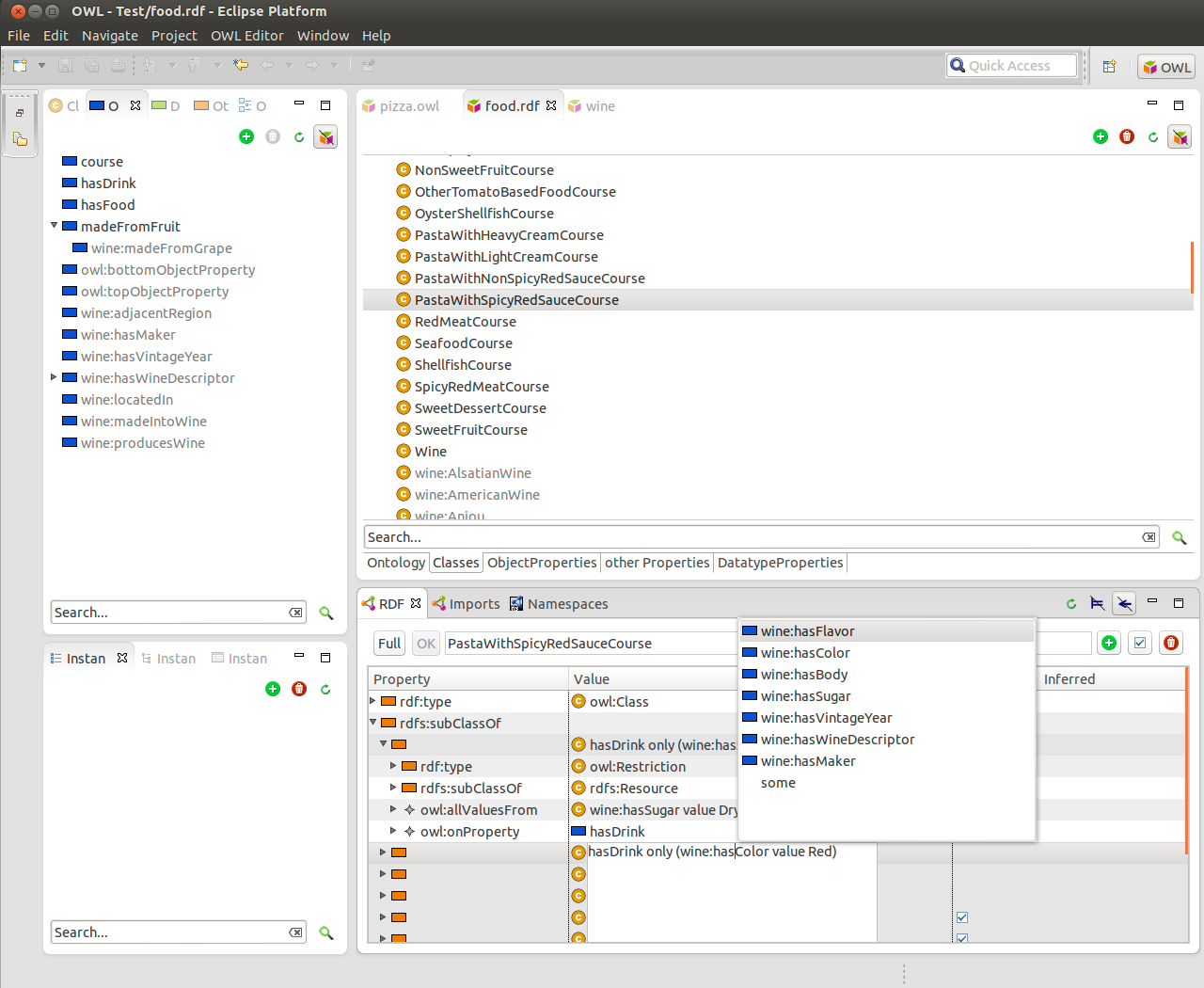
Fresnel Editor allows the user to visualize RDF data using W3C Fresnel vocabulary. It provides Swing GUI simplifying creation and editing of Fresnel Lenses, Formats and Groups and allows the user to use them to visualize RDF data as XHTML web page.
Furthermore, RDFaCE employs Sindice, Swoogle and Prefix.cc APIs for resource suggestion (providing appropriate URIs for subjects, properties and namespaces).Another feature supported by RDFaCE is combining the results of multiple NLP APIs. Using this approach, we can harness synergies arising from the combination of different approaches for automatic text annotation. Currently, RDFaCE supports 7 NLP APIs namely Alchemy,Extractiv, Open Calais, Ontos,Evri, Saplo,Lupedia and DBpedia spotlight.
The RDFaCE approach is very versatile and can be applied in a vast number of use cases. rNews, Ontowiki and Wordpress are three use cases of RDFaCE.
RDFaCE-Lite is a lite version of RDFaCE which is specifically developed to support the rNews standard for annotating news and blog posts. It supports user-friendly editing of entities by only one click. It also provides support for Microdata (according to Schema.org) as an alternative annotation format.The demo is available at http://rdface.aksw.org/lite/.
The normal annotation process in RDFaCE consists of four steps:
- Defining appropriate namespaces by clicking button.
- Selecting a fragment of the text.
- Assigning the subject (and type) to be used for the selected fragment by clicking button.
- Inserting triples by assigning properties using button.
Triples can be seen by launching the triple browser ( button).You can go to setting and select one or multiple NLP APIs plus your combination strategy to automatically annotate your content by clicking .To see a report on the entities found by each API, you can press after determining your desired combination.To instantly add a triple using rNews vocabulary, just select a part of the text and then on the context menu (which appears on mouse right click) select your desired type or property.

You can download the beta version of RDFaCE from here.RDFaCE is also available as a Wordpress Plugin.
To configure RDFaCE plugin you need to follow the normal procedure of adding a plugin in Tiny MCE (More info...).To enable automatic annotation, you need to register for each API and get an API key for it.Then go to RDFaCEphp folder and open proxy.php file. In this file you can set API keys for your desirable enrichment APIs. You can register for current five available APIs at:

Then you need to go to rdface/js/util/config.php and set the path of your proxy file.
- NIF (http://aksw.org/Projects/NIF)
- FOX (http://aksw.org/Projects/FOX)
| Filename extension | |
|---|---|
| Internet media type | text/turtle |
| Developed by | Dave Beckett |
| Latest release | |
| Type of format | Semantic Web |
| Container for | RDF data |
| Extended from | N-Triples, Notation3 |
| Extended to | TriG_(syntax) |
| Website | www.w3.org/TR/turtle/ |
Terse RDF Triple Language (Turtle) is a syntax and file format for expressing data in the Resource Description Framework (RDF) data model. Turtle syntax is similar to that of SPARQL, an RDF query language. It is a common data format for storing RDF data, along with N-Triples, JSON-LD and RDF/XML.

RDF represents information using semantic triples, which comprise a subject, predicate, and object. Each item in the triple is expressed as a Web URI. Turtle provides a way to group three URIs to make a triple, and provides ways to abbreviate such information, for example by factoring out common portions of URIs. For example, information about Huckleberry Finn could be expressed as:
History[edit]
Turtle was defined by Dave Beckett as a subset of Tim Berners-Lee and Dan Connolly's Notation3 (N3) language, and a superset of the minimal N-Triples format. Unlike full N3, which has an expressive power that goes much beyond RDF, Turtle can only serialize valid RDF graphs. Turtle is an alternative to RDF/XML, the originally unique syntax and standard for writing RDF. As opposed to RDF/XML, Turtle does not rely on XML and is generally recognized as being more readable and easier to edit manually than its XML counterpart.
SPARQL, the query language for RDF, uses a syntax similar to Turtle for expressing query patterns.
In 2011, a working group of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) started working on an updated version of RDF, with the intention of publishing it along with a standardised version of Turtle. This Turtle specification was published as a W3C Recommendation on 25 February 2014.[1]
A significant proportion of RDF toolkits include Turtle parsing and serializing capability. Some examples of such toolkits are Redland, RDF4J, Jena, Python's RDFLib and JavaScript's N3.js.
Example[edit]
The following example defines 3 prefixes ('rdf', 'dc', and 'ex'), and uses them in expressing a statement about the editorship of the RDF/XML document:
(Turtle examples are also valid Notation3).
The example encodes an RDF graph made of four triples, which express these facts:
- The W3C technical report on RDF syntax and grammar has the title RDF/XML Syntax Specification (Revised).
- That report's editor is a certain individual, who in turn
- Has full name Dave Beckett.
- Has a home page at a certain place.
Here are the triples made explicit in N-Triples notation:
The MIME type of Turtle is text/turtle. The character encoding of Turtle content is always UTF-8.[2]
Named graphs[edit]
Rdf Editor Gui
TriG RDF syntax extends Turtle with support for named graphs.
See also[edit]
Rdf Editor Free
References[edit]
- ^'RDF 1.1 Turtle - Terse RDF Triple LanguageTurtle'. World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). 25 February 2014. Retrieved 16 December 2015.
- ^'MIME Media Types: text/turtle'. Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). 28 March 2011. Retrieved 27 November 2011.